Brianna Goodwin was selected as a finalist in the MS-level Student Paper Competition at the Summer Biomechanics, Bioengineering and Biotransport Conference (SB3C) this summer. She was one of 27 finalists selected for this competition. Congratulations and good luck to Brianna!
Brianna Goodwin was selected as a finalist in the MS-level Student Paper Competition at the Summer Biomechanics, Bioengineering and Biotransport Conference (SB3C) this summer. She was one of 27 finalists selected for this competition. Congratulations and good luck to Brianna!
Publications
KM Steele, ME Munger, KM Peters, BR Shuman, MH Schwartz (2019) “Repeatability of electromyography recordings and muscle synergies during gait among children with cerebral palsy.” Gait & Posture
Journal Article in Gait & Posture:
Repeatability of EMG is similar between typically developing children and children with cerebral palsy.
 Background: Clinical gait analysis is commonly used in the evaluation and treatment of children with cerebral palsy (CP). While the repeatability of kinematic and kinetic measures of gait has previously been evaluated, the repeatability of electromyography (EMG) recordings or measures calculated from EMG data, such as muscle synergies, remains unclear for this population.
Background: Clinical gait analysis is commonly used in the evaluation and treatment of children with cerebral palsy (CP). While the repeatability of kinematic and kinetic measures of gait has previously been evaluated, the repeatability of electromyography (EMG) recordings or measures calculated from EMG data, such as muscle synergies, remains unclear for this population.
Research Question: Are EMG recordings and muscle synergies from clinical gait analysis repeatable between visits for children with CP?
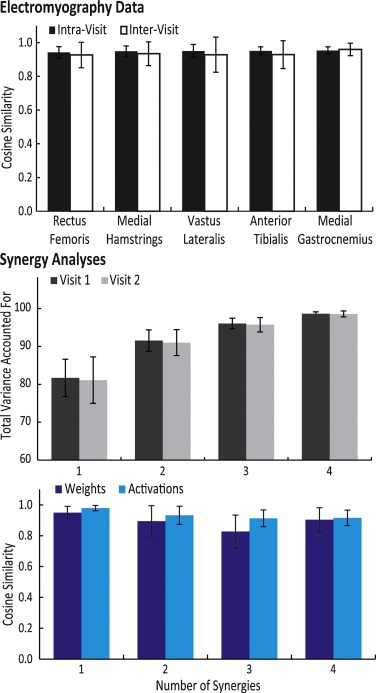
Methods: We recruited 20 children with bilateral CP who had been referred for clinical gait analysis. The children completed two visits less than six weeks apart with EMG data collected bilaterally from five muscles (rectus femoris, medial hamstrings, vastus lateralis, anterior tibialis, and medial gastrocnemius). Variance ratio and cosine similarity were used to evaluate repeatability of EMG waveforms between visits. Nonnegative matrix factorization was used to calculate synergies from EMG data at each visit to compare synergy weights and activations.
Results & significance: The inter-visit variance ratios of EMG data for children with CP were similar to previously reported results for typically-developing children and unimpaired adults (range: 0.39 for vastus lateralis to 0.66 for rectus femoris). The average cosine similarity of the EMG waveforms between visits was greater than 0.9 for all muscles, while synergy weights and activations also had high similarity – greater than 0.8 and 0.9 between visits, respectively. These results demonstrate that EMG repeatability between visits during clinical gait analysis for children with CP is similar to unimpaired individuals. These results provide a baseline for evaluating whether observed changes in EMG recordings between visits reflect real changes in muscle activity or are within the range of inter-visit variability.
BR Shuman, M Goudriaan, K Desloovere, MH Schwartz, KM Steele (2018) “Associations Between Muscle Synergies and Treatment Outcomes in Cerebral Palsy Are Robust Across Clinical Centers.” Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
Journal article in Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation:
In collaboration with Gillette Children’s Hospital and University Hospital Pellenberg we examined whether associations between treatment outcomes and muscles synergies are robust between clinical centers.
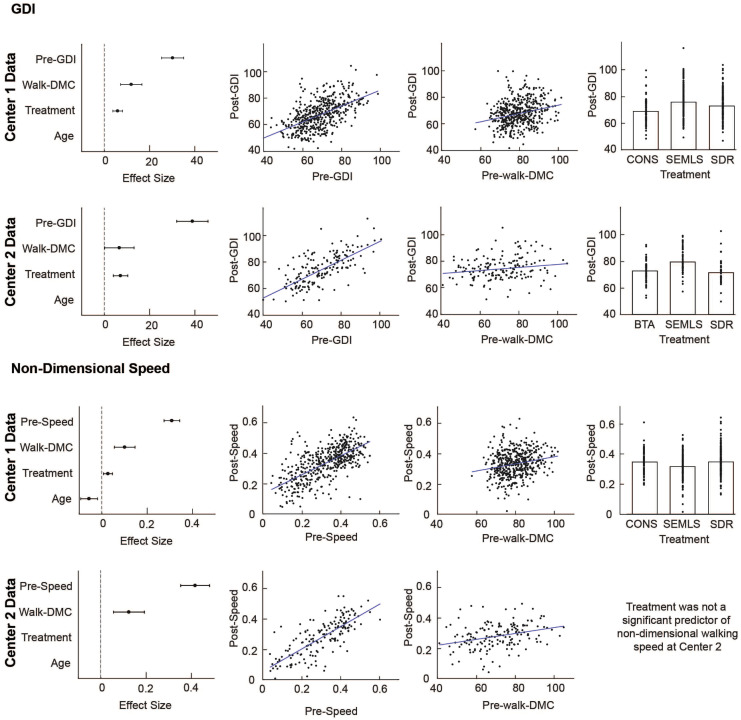 Objective: To determine whether patient-specific differences in motor control quantified using muscle synergy analysis were associated with changes in gait after treatment of cerebral palsy (CP) across 2 clinical centers with different treatments and clinical protocols.
Objective: To determine whether patient-specific differences in motor control quantified using muscle synergy analysis were associated with changes in gait after treatment of cerebral palsy (CP) across 2 clinical centers with different treatments and clinical protocols.Alyssa Spomer and Momona Yamagami Present at a Neurorehabilitation Conference in Spain
Alyssa and Momona attended the Summer School on Neurorehabilitation (SSNR) in Baiona, Spain from September 16th to the 21st. Alyssa gave a podium presentation on a feedback system she is developing that aims to characterize and target altered motor control in cerebral palsy. Momona gave a poster presentation to share her recent quantifications of deficits in motor planning in cerebral palsy. Nice work, Alyssa and Momona!
Research Experience Undergraduates Present at CSNE
This summer the Steele Lab had the pleasure of hosting three undergraduate researchers – Julia Costacurta from Johns Hopkins, Joe Lawler from the University of Washington, and Preston Pan from the University of Washington.
After a competitive selection process, students are offered a 10-week internship here at the University to work directly with a research lab on campus. One of the program’s final deliverables is a presentation of their work, both in podium and poster format, to members of the local and scientific community. Congratulations to Julia, Joe, and Preston for their successful time here in the lab, and for giving polished presentations.
Julia’s work explored the impacts of Ankle-Foot Orthoses on transient gait, a period of walking where little is currently known about device dynamics.
 Preston worked directly with Seattle Children’s Hospital to implement algorithms for detecting bimanual hand movement before, during, and after a common therapy used to promote improved motor skills for children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy.
Preston worked directly with Seattle Children’s Hospital to implement algorithms for detecting bimanual hand movement before, during, and after a common therapy used to promote improved motor skills for children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy.
Joe’s focus this summer involved working with the University of Washington HuskyADAPT program. HuskyADAPT is a student-run program in its second year and stands for Accessible Design and Play Technology. Joe’s research question asked, how we can improve upon and further promote an inclusive and sustainable program for assistive technology?