Journal Article in PLoS ONE
There is growing interest in the use of biofeedback-augmented gait training in cerebral palsy (CP). Audiovisual, sensorimotor, and immersive biofeedback paradigms are commonly used to elicit short-term gait improvements; however, outcomes remain variable. Because biofeedback training requires that individuals have the capacity to both adapt their gait in response to feedback and retain improvements across sessions, changes in either capacity may affect outcomes. Yet, neither has been explored extensively in CP.
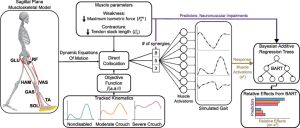
 Aim: The aim of this study was to evaluate the extent to which individuals with CP adapt gait and retain improvements during multi-session practice with a multimodal biofeedback paradigm, designed to promote plantarflexor recruitment. Secondarily, we compared overground walking performance before and after biofeedback sessions to understand if any observed in-session improvements were transferred.
Aim: The aim of this study was to evaluate the extent to which individuals with CP adapt gait and retain improvements during multi-session practice with a multimodal biofeedback paradigm, designed to promote plantarflexor recruitment. Secondarily, we compared overground walking performance before and after biofeedback sessions to understand if any observed in-session improvements were transferred.
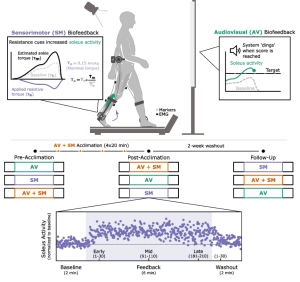
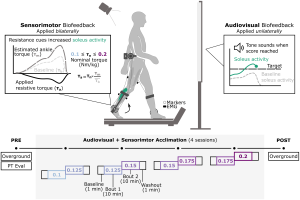
Methods: In this study, we evaluated the extent to which adolescents with CP (7M/1F; 14 years (12.5,15.26)) could adapt gait and retain improvements across four, 20-minute sessions using combined audiovisual and sensorimotor biofeedback. Both systems were designed to target plantarflexor activity. Audiovisual biofeedback displayed real-time soleus activity and sensorimotor biofeedback was provided using a bilateral resistive ankle exoskeleton. We quantified the time-course of change in muscle activity within and across sessions and overground walking function before and after the four sessions.
Results: All individuals were able to significantly increase soleus activity from baseline using multimodal biofeedback (p < 0.031) but demonstrated heterogeneous adaptation strategies. In-session soleus adaptation had a moderate positive correlation with short-term retention of the adapted gait patterns (0.40 ≤ ρ ≤ 0.81), but generally weak correlations with baseline walking function (GMFCS Level) and motor control complexity (ρ ≤ 0.43). The latter indicates that adaptation capacity may be a critical and unique metric underlying response to biofeedback. Notably, in-session gains did not correspond to significant improvements in overground walking function (p > 0.11).
Interpretation: This work suggests that individuals with CP have the capacity to adapt their gait using biofeedback, but responses are highly variable. Characterizing the factors driving adaptation to biofeedback may be a promising avenue to understand the heterogeneity of existing biofeedback training outcomes and inform future system optimization for integration into clinical care.