Journal Article in ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI) 2020 Preceedings:
These results suggest that control theory modeling can provide a platform to successfully quantify device performance in the absence of errors arising from motor impairments
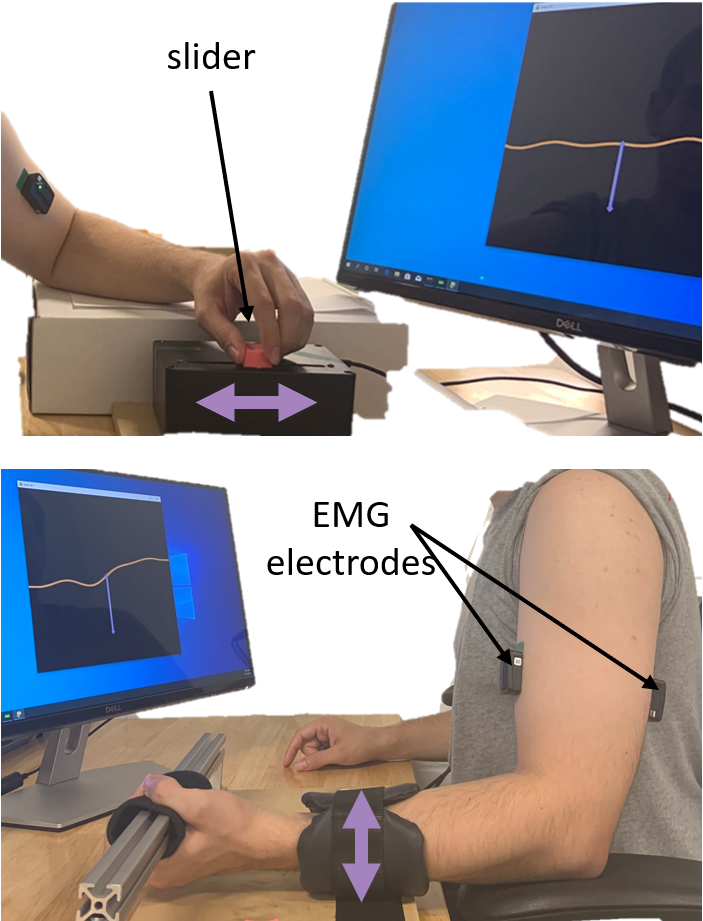
Photo (top and bottom) of a user using a slider (top) and muscles (bottom) to control a cursor on the screen.
(Top image) Side image of user. User rests their elbow and pinches the slider and moves the slider towards and away from their body to control the cursor.
(Bottom image) Side image of user. User is strapped to a rigid device holding a bar with hands supinated towards the ceiling, with the forearms at a 90 degree angle from the upper arms.
Electrodes are placed on the biceps and triceps and labelled. Arrows pointing up and down indicate that users move their arm up and down to control the cursor.
Background: Manual device interaction requires precise coordination which may be difficult for users with motor impairments. Muscle interfaces provide alternative interaction methods that may enhance performance, but have not yet been evaluated for simple (eg. mouse tracking) and complex (eg. driving) continuous tasks. Control theory enables us to probe continuous task performance by separating user input into intent and error correction to quantify how motor impairments impact device interaction
Aim: Propose and extend an experimental and analytical method to guide future development of accessible interfaces like muscle interfaces using control theory
Method: We compared the effectiveness of a manual versus a muscle interface for eleven users without and three users with motor impairments performing continuous tasks.
Results: Both user groups preferred and performed better with the muscle versus the manual interface for the complex continuous task.
Interpretation: Results suggest muscle interfaces and algorithms that can detect and augment user intent may be especially useful for future design of interfaces for continuous tasks.
Momona also gave a phenomenal talk on this paper last week in the University of Washington’s ‘DUB Shorts’ series (video posted below). Nice job Momona!