Journal Article in IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering
Powered mobility technology can be a powerful tool to facilitate self-initiated exploration and play for toddlers with motor disabilities. The joystick-controlled Permobil Explorer Mini is currently the only commercially available powered mobility device for children ages 1-3 years in the United States. However, many open questions persist regarding how joystick-based mobility technologies should be designed to optimally suit the developmental needs of toddlers.
 Aim: The purpose of this study was to quantify how toddlers with motor disabilities use the Explorer Mini during free exploration and play.
Aim: The purpose of this study was to quantify how toddlers with motor disabilities use the Explorer Mini during free exploration and play.
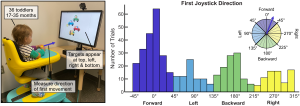
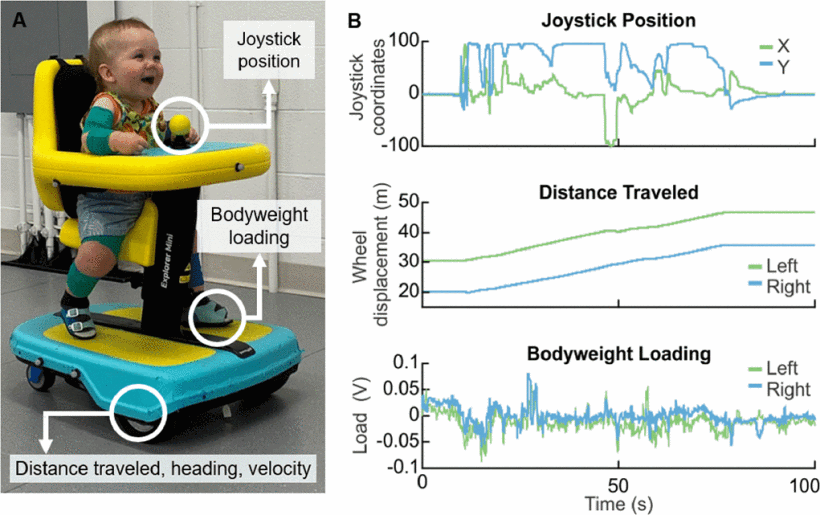
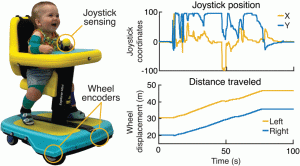
Methods: For this work, we developed a custom-instrumented Explorer Mini with embedded sensors to measure joystick interactions and wheel rotations. Nine children with motor disabilities (ages 12-36 months) participated in 12 in-lab visits, and during each visit they engaged in two 15-20 minute play sessions. For each session, we calculated several quantitative outcome metrics, including the time spent using the joystick, distance traveled, and the number, duration, and complexity of joystick interactions.
Results: Every participant independently interacted with the joystick and moved the Explorer Mini during every session. Over 12 visits, participants significantly increased their distance traveled and the time spent with the joystick active. Surprisingly, we found that only 48% of joystick interactions resulted in device movement, which has important implications for learning.
Interpretation: These results can serve as a benchmark for caregivers and clinicians to understand early device use patterns. Furthermore, this knowledge can be used to inform the design of new powered mobility technologies for toddlers with disabilities or support the refinement of existing devices.