Journal article in Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience:
Filtering parameters impact the results from muscle synergy analyses.
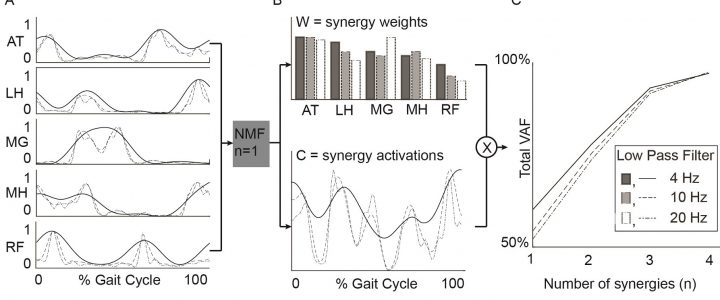
A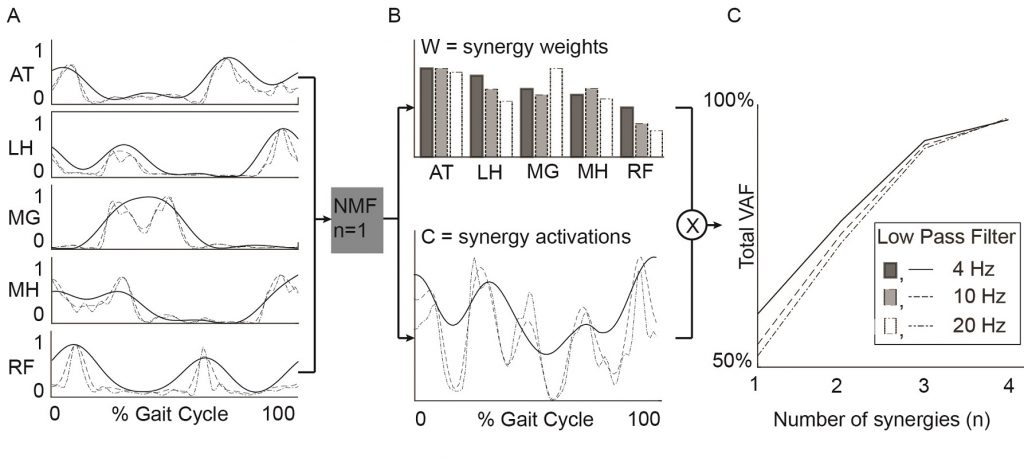 bstract: Muscle synergies calculated from electromyography (EMG) data identify weighted groups of muscles activated together during functional tasks. Research has shown that fewer synergies are required to describe EMG data of individuals with neurologic impairments. When considering potential clinical applications of synergies, understanding how EMG data processing impacts results and clinical interpretation is important. The aim of this study was to evaluate how EMG signal processing impacts synergy outputs during gait. We evaluated the impacts of two common processing steps for synergy analyses: low pass (LP) filtering and unit variance scaling. We evaluated EMG data collected during barefoot walking from five muscles of 113 children with cerebral palsy (CP) and 73 typically-developing (TD) children. We applied LP filters to the EMG data with cutoff frequencies ranging from 4 to 40 Hz (reflecting the range reported in prior synergy research). We also evaluated the impact of normalizing EMG amplitude by unit variance. We found that the total variance accounted for (tVAF) by a given number of synergies was sensitive to LP filter choice and decreased in both TD and CP groups with increasing LP cutoff frequency (e.g., 9.3 percentage points change for one synergy between 4 and 40 Hz). This change in tVAF can alter the number of synergies selected for further analyses. Normalizing tVAF to a z-score (e.g., dynamic motor control index during walking, walk-DMC) reduced sensitivity to LP cutoff. Unit variance scaling caused comparatively small changes in tVAF. Synergy weights and activations were impacted less than tVAF by LP filter choice and unit variance normalization. These results demonstrate that EMG signal processing methods impact outputs of synergy analysis and z-score based measures can assist in reporting and comparing results across studies and clinical centers.
bstract: Muscle synergies calculated from electromyography (EMG) data identify weighted groups of muscles activated together during functional tasks. Research has shown that fewer synergies are required to describe EMG data of individuals with neurologic impairments. When considering potential clinical applications of synergies, understanding how EMG data processing impacts results and clinical interpretation is important. The aim of this study was to evaluate how EMG signal processing impacts synergy outputs during gait. We evaluated the impacts of two common processing steps for synergy analyses: low pass (LP) filtering and unit variance scaling. We evaluated EMG data collected during barefoot walking from five muscles of 113 children with cerebral palsy (CP) and 73 typically-developing (TD) children. We applied LP filters to the EMG data with cutoff frequencies ranging from 4 to 40 Hz (reflecting the range reported in prior synergy research). We also evaluated the impact of normalizing EMG amplitude by unit variance. We found that the total variance accounted for (tVAF) by a given number of synergies was sensitive to LP filter choice and decreased in both TD and CP groups with increasing LP cutoff frequency (e.g., 9.3 percentage points change for one synergy between 4 and 40 Hz). This change in tVAF can alter the number of synergies selected for further analyses. Normalizing tVAF to a z-score (e.g., dynamic motor control index during walking, walk-DMC) reduced sensitivity to LP cutoff. Unit variance scaling caused comparatively small changes in tVAF. Synergy weights and activations were impacted less than tVAF by LP filter choice and unit variance normalization. These results demonstrate that EMG signal processing methods impact outputs of synergy analysis and z-score based measures can assist in reporting and comparing results across studies and clinical centers.