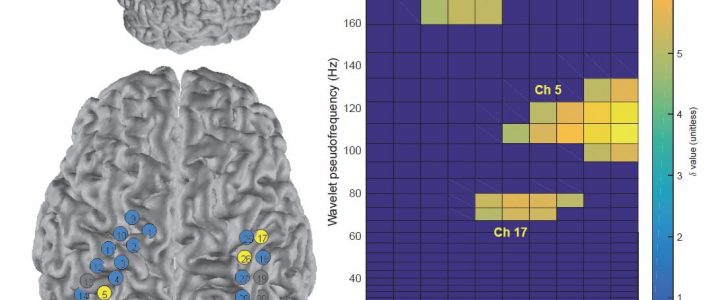
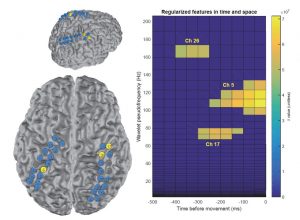
Journal article in the Journal of Medical Case Reports:
A case study of crouch gait over 8-years in a child with no surgical interventions.
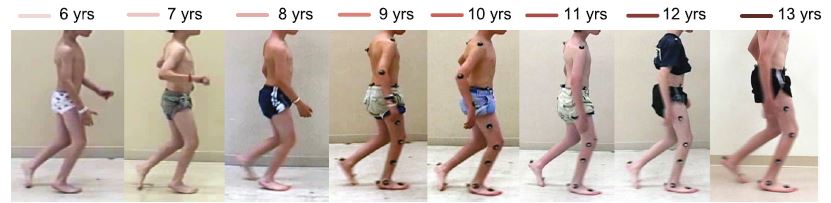
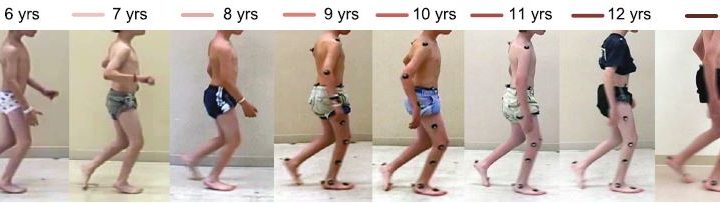
Background: This case report provides a unique look at the progression of crouch gait in a child with cerebral palsy over an 8-year time period, through annual physical examinations, three-dimensional gait analyses, and evaluation of postural balance. Our patient received regular botulinum toxin-A injections, casting, and physical therapy but no surgical interventions.
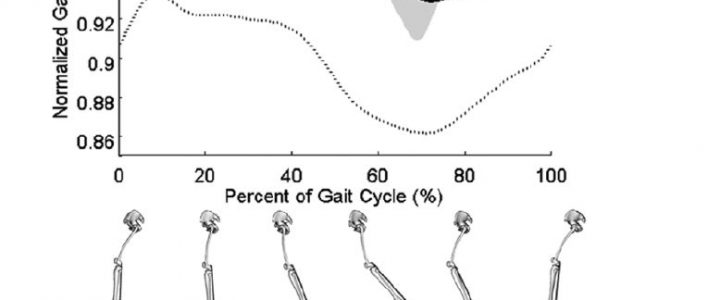
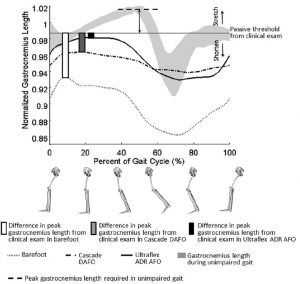
Case presentation: A white American boy with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy was evaluated annually by clinical motion analyses, including physical examination, joint kinematics, electromyography, energy expenditure, and standing postural balance tests, from 6 to 13 years of age. These analyses revealed that the biomechanical factors contributing to our patient’s crouch gait were weak plantar flexors, short and spastic hamstrings, moderately short hip flexors, and external rotation of the tibiae. Despite annual recommendations for surgical lengthening of the hamstrings, the family opted for non-surgical treatment through botulinum toxin-A injections, casting, and exercise. Our patient’s crouch gait improved between ages 6 and 9, then worsened at age 10, concurrent with his greatest body mass index, increased plantar flexor weakness, increased standing postural sway, slowest normalized walking speed, and greatest walking energy expenditure. Although our patient’s maximum knee extension in stance improved by 14 degrees at 13 years of age compared to 6 years of age, peak knee flexion in swing declined, his ankles became more dorsiflexed, his hips became more internally rotated, and his tibiae became more externally rotated. From 6 to 9 years of age, our patient’s minimum stance-phase knee flexion varied in an inverse relationship with his body mass index; from 10 to 13 years of age, changes in his minimum stance-phase knee flexion paralleled changes in his body mass index.
Conclusions: The motor deficits of weakness, spasticity, shortened muscle-tendon lengths, and impaired selective motor control were highlighted by our patient’s clinical motion analyses. Overall, our patient’s crouch gait improved mildly with aggressive non-operative management and a supportive family dedicated to regular home exercise. The annual clinical motion analyses identified changes in motor deficits that were associated with changes in the child’s walking pattern, suggesting that these analyses can serve to track the progression of children with spastic cerebral palsy.
 Abstract: Spinal Muscular Atrophy is the most common genetic cause of infant death. Due to its severity, there is a need for methods for automated estimation of disease progression. In this paper we propose a Convolutional-Neural-Network (CNN) model to estimate disease progression during infants’ natural behavior. With the proposed methodology, we were able to predict each child’s score on current behavior-based clinical exams with an average per-subject error of 6.96 out of 72 points (<10 % difference), using 30-second videos in leave-one-subject-out-cross-validation setting. When simple statistics were used over 30-second video-segments to estimate a score for longer videos, we obtained an average error of 5.95 (∼8 % error rate). By showing promising results on a small dataset (N = 70, 2-minute samples, which were handled as 1487, 30-second video segments), our methodology demonstrates that it is possible to benefit from CNNs on small datasets by proper design and data handling choices.
Abstract: Spinal Muscular Atrophy is the most common genetic cause of infant death. Due to its severity, there is a need for methods for automated estimation of disease progression. In this paper we propose a Convolutional-Neural-Network (CNN) model to estimate disease progression during infants’ natural behavior. With the proposed methodology, we were able to predict each child’s score on current behavior-based clinical exams with an average per-subject error of 6.96 out of 72 points (<10 % difference), using 30-second videos in leave-one-subject-out-cross-validation setting. When simple statistics were used over 30-second video-segments to estimate a score for longer videos, we obtained an average error of 5.95 (∼8 % error rate). By showing promising results on a small dataset (N = 70, 2-minute samples, which were handled as 1487, 30-second video segments), our methodology demonstrates that it is possible to benefit from CNNs on small datasets by proper design and data handling choices.