Journal Article in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience:
Despite significant differences in kinematics children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy have similar control complexity to typically developing children.
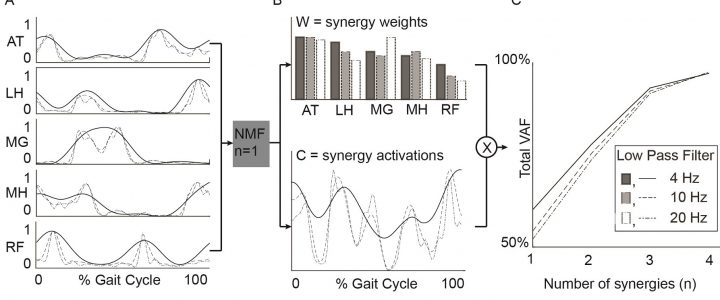
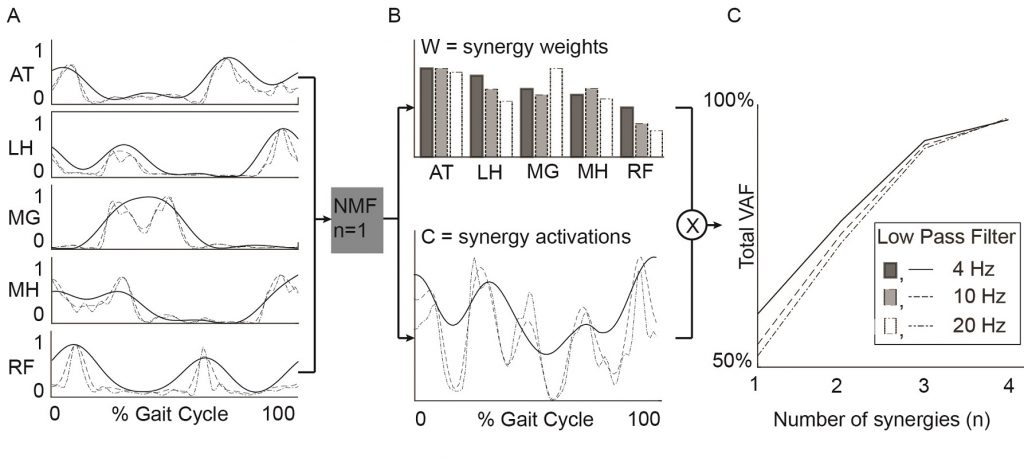
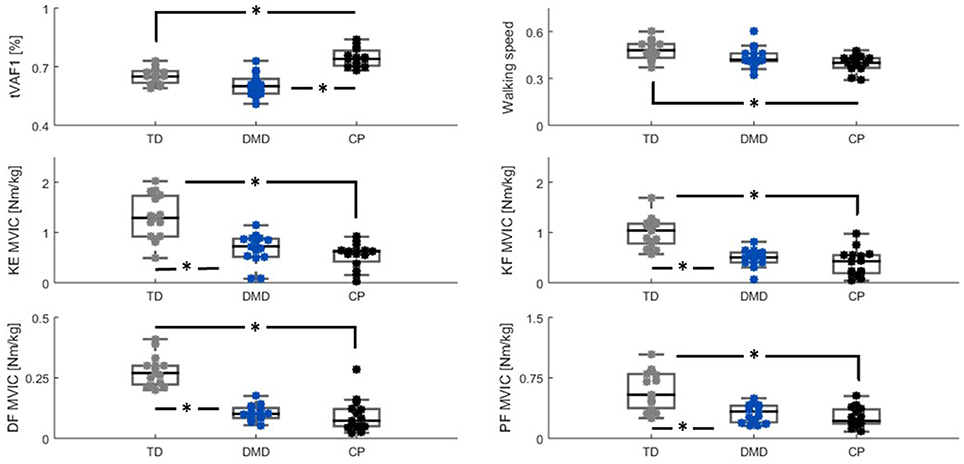 Abstract: Cerebral palsy (CP) and Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) are neuromuscular disorders characterized by muscle weakness. Weakness in CP has neural and non-neural components, whereas in DMD, weakness can be considered as a predominantly non-neural problem. Despite the different underlying causes, weakness is a constraint for the central nervous system when controlling gait. CP demonstrates decreased complexity of motor control during gait from muscle synergy analysis, which is reflected by a higher total variance accounted for by one synergy (tVAF1). However, it remains unclear if weakness directly contributes to higher tVAF1 in CP, or whether altered tVAF1 reflects mainly neural impairments. If muscle weakness directly contributes to higher tVAF1, then tVAF1 should also be increased in DMD. To examine the etiology of increased tVAF1, muscle activity data of gluteus medius, rectus femoris, medial hamstrings, medial gastrocnemius, and tibialis anterior were measured at self-selected walking speed, and strength data from knee extensors, knee flexors, dorsiflexors and plantar flexors, were analyzed in 15 children with CP [median (IQR) age: 8.9 (2.2)], 15 boys with DMD [8.7 (3.1)], and 15 typical developing (TD) children [8.6 (2.7)]. We computed tVAF1 from 10 concatenated steps with non-negative matrix factorization, and compared tVAF1between the three groups with a Mann-Whiney U-test. Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients were used to determine if weakness in specific muscle groups contributed to altered tVAF1. No significant differences in tVAF1 were found between DMD [tVAF1: 0.60 (0.07)] and TD children [0.65 (0.07)], while tVAF1 was significantly higher in CP [(0.74 (0.09)] than in the other groups (both p < 0.005). In CP, weakness in the plantar flexors was related to higher tVAF1 (r = −0.72). In DMD, knee extensor weakness related to increased tVAF1 (r = −0.50). These results suggest that the non-neural weakness in DMD had limited influence on complexity of motor control during gait and that the higher tVAF1 in children with CP is mainly related to neural impairments caused by the brain lesion.
Abstract: Cerebral palsy (CP) and Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) are neuromuscular disorders characterized by muscle weakness. Weakness in CP has neural and non-neural components, whereas in DMD, weakness can be considered as a predominantly non-neural problem. Despite the different underlying causes, weakness is a constraint for the central nervous system when controlling gait. CP demonstrates decreased complexity of motor control during gait from muscle synergy analysis, which is reflected by a higher total variance accounted for by one synergy (tVAF1). However, it remains unclear if weakness directly contributes to higher tVAF1 in CP, or whether altered tVAF1 reflects mainly neural impairments. If muscle weakness directly contributes to higher tVAF1, then tVAF1 should also be increased in DMD. To examine the etiology of increased tVAF1, muscle activity data of gluteus medius, rectus femoris, medial hamstrings, medial gastrocnemius, and tibialis anterior were measured at self-selected walking speed, and strength data from knee extensors, knee flexors, dorsiflexors and plantar flexors, were analyzed in 15 children with CP [median (IQR) age: 8.9 (2.2)], 15 boys with DMD [8.7 (3.1)], and 15 typical developing (TD) children [8.6 (2.7)]. We computed tVAF1 from 10 concatenated steps with non-negative matrix factorization, and compared tVAF1between the three groups with a Mann-Whiney U-test. Spearman’s rank correlation coefficients were used to determine if weakness in specific muscle groups contributed to altered tVAF1. No significant differences in tVAF1 were found between DMD [tVAF1: 0.60 (0.07)] and TD children [0.65 (0.07)], while tVAF1 was significantly higher in CP [(0.74 (0.09)] than in the other groups (both p < 0.005). In CP, weakness in the plantar flexors was related to higher tVAF1 (r = −0.72). In DMD, knee extensor weakness related to increased tVAF1 (r = −0.50). These results suggest that the non-neural weakness in DMD had limited influence on complexity of motor control during gait and that the higher tVAF1 in children with CP is mainly related to neural impairments caused by the brain lesion.