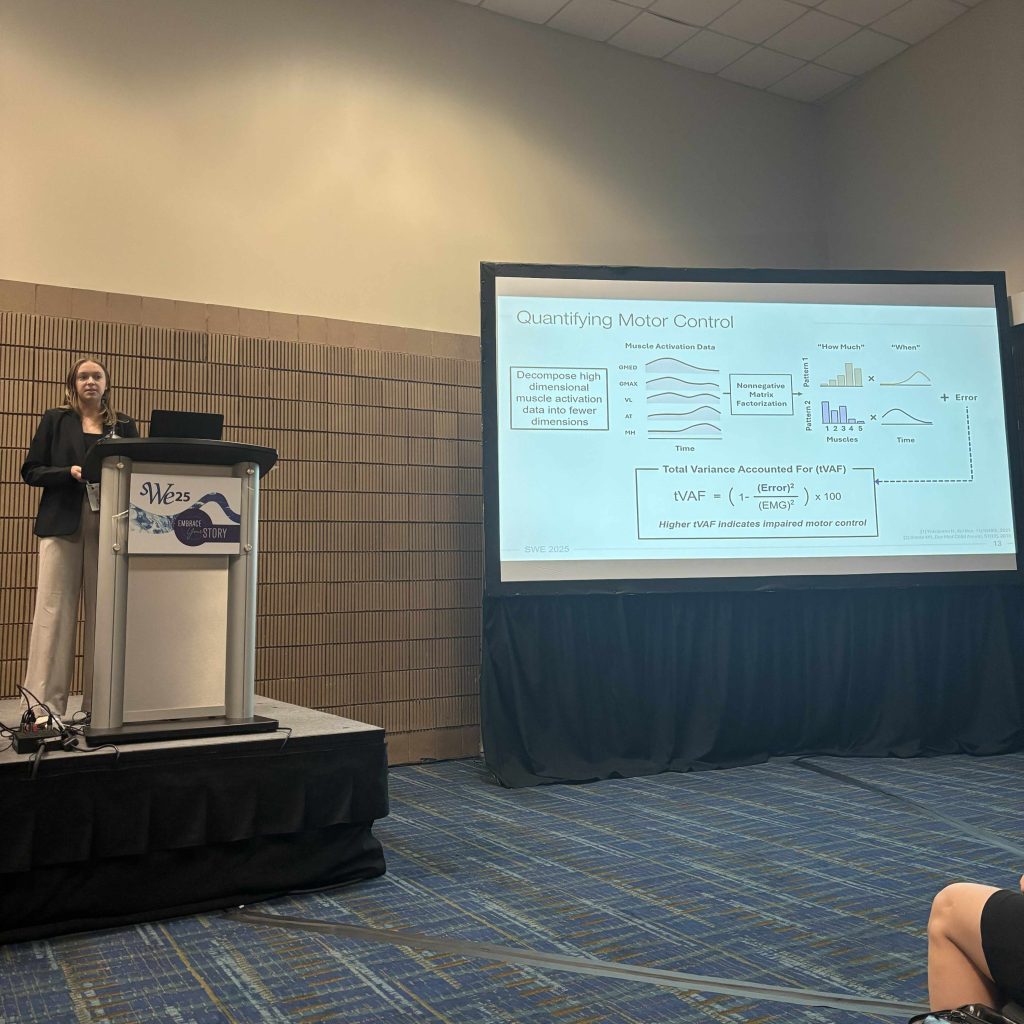
Mia Hoffman of the Neuromechanics & Mobility Lab, along with Bethany M. Sloane, Postdoctoral Scholar at the University of Washington’s Center for Research and Education on Accessible Technology and Experiences (CREATE), presented a session at the APTA Pediatrics 2025 Conference titled “Reimagining Mobility Aids: Collaborative Innovations Between Engineering and Physical Therapy.”
The session explored how interdisciplinary partnerships can transform traditional mobility aids into creative, user-centered solutions. Real-world examples included 3D-printed joystick adaptations, sensor-integrated systems, and community loaner programs. Attendees engaged in design thinking activities and left with practical tools to reimagine mobility for young children.