Journal Article in Prosthetics & Orthotics International
Background
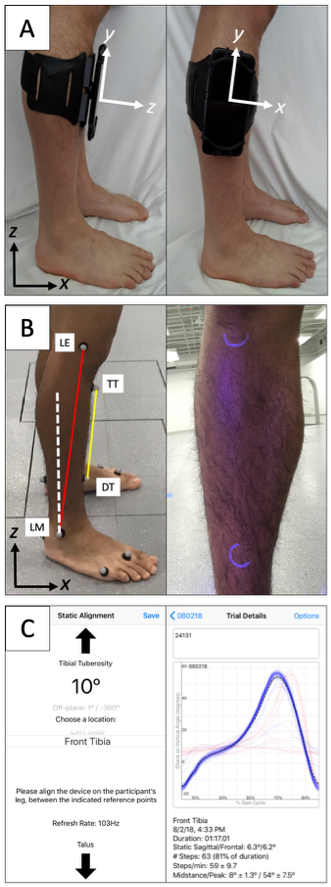
Assessments of human movement are clinically important. However, accurate measurements are often unavailable due to the need for expensive equipment or intensive processing. For orthotists and therapists, shank-to-vertical angle (SVA) is one critical measure used to assess gait and guide prescriptions. Smartphone-based sensors may provide a widely-available platform to expand access to quantitative assessments.
Objectives
Assess accuracy and repeatability of smartphone-based measurement of SVA compared to marker-based 3D motion analysis.
Method
Four licensed clinicians (two physical therapists and two orthotists) measured SVA during gait with a smartphone attached to the anterior or lateral shank surface of unimpaired adults. We compared SVA calculated from the smartphone’s inertial measurement unit to marker-based measurements. Each clinician completed three sessions/day on two days with each participant to assess repeatability.
Results
Average absolute differences in SVA measured with a smartphone versus marker-based 3D motion analysis during gait were 0.67 ± 0.25° and 4.89 ± 0.72°, with anterior or lateral smartphone positions, respectively. The inter- and intra-day repeatability of SVA were within 2° for both smartphone positions.
Conclusions
Smartphone sensors can be used to measure SVA with high accuracy and repeatability during unimpaired gait, providing a widely-available tool for quantitative gait assessments.
Try it out!
The app for monitoring shank-to-vertical angle is available for you to download and use on either Android or iOS smartphone. Please complete THIS SURVEY which will then send you an e-mail with instructions for installation and use. This app is not an FDA approved medical device and should be used appropriately.