Journal Article in Scientific Reports
Ankle exoskeletons alter whole-body walking mechanics, energetics, and stability by altering center-of-mass (CoM) motion. Controlling the dynamics governing CoM motion is, therefore, critical for maintaining efficient and stable gait. However, how CoM dynamics change with ankle exoskeletons is unknown, and how to optimally model individual-specific CoM dynamics, especially in individuals with neurological injuries, remains a challenge.
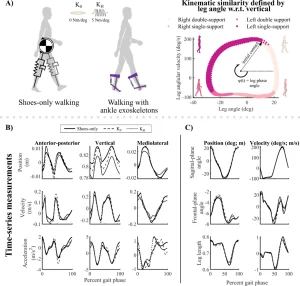 Aim: Evaluate individual-specific changes in CoM dynamics in unimpaired adults and one individual with post-stroke hemiparesis while walking in shoes-only and with zero-stiffness and high-stiffness passive ankle exoskeletons.
Aim: Evaluate individual-specific changes in CoM dynamics in unimpaired adults and one individual with post-stroke hemiparesis while walking in shoes-only and with zero-stiffness and high-stiffness passive ankle exoskeletons.
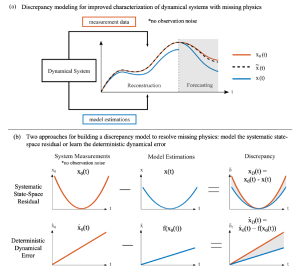
Methods: To identify optimal sets of physically interpretable mechanisms describing CoM dynamics, termed template signatures, we leveraged hybrid sparse identification of nonlinear dynamics (Hybrid-SINDy), an equation-free data-driven method for inferring sparse hybrid dynamics from a library of candidate functional forms.
Results: In unimpaired adults, Hybrid-SINDy automatically identified spring-loaded inverted pendulum-like template signatures, which did not change with exoskeletons (p > 0.16), except for small changes in leg resting length (p < 0.001). Conversely, post-stroke paretic-leg rotary stiffness mechanisms increased by 37–50% with zero-stiffness exoskeletons.
Interpretation: While unimpaired CoM dynamics appear robust to passive ankle exoskeletons, how neurological injuries alter exoskeleton impacts on CoM dynamics merits further investigation. Our findings support Hybrid-SINDy’s potential to discover mechanisms describing individual-specific CoM dynamics with assistive devices.