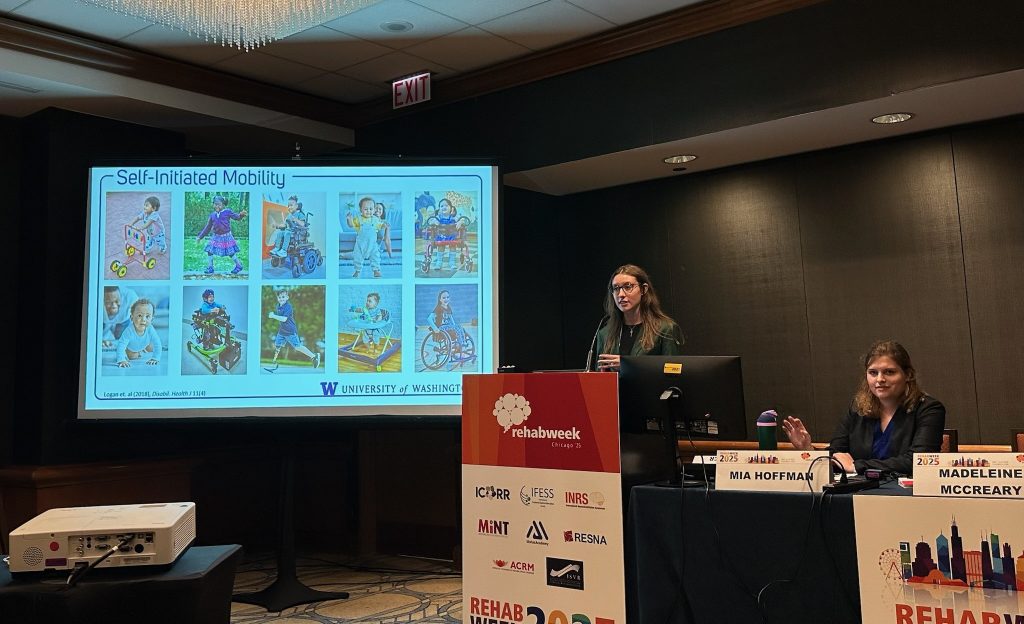
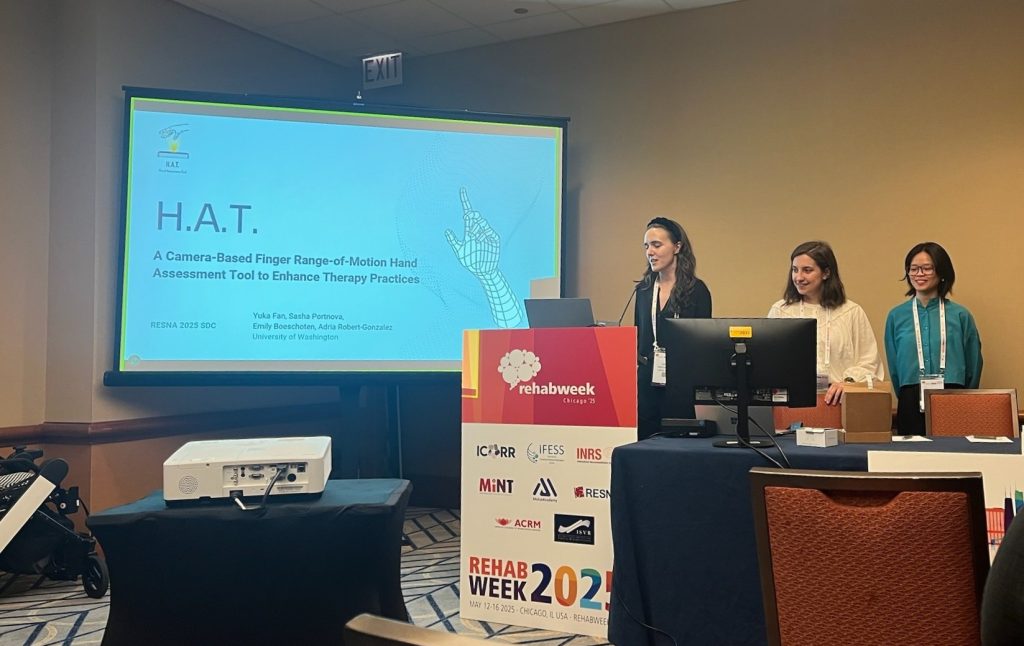
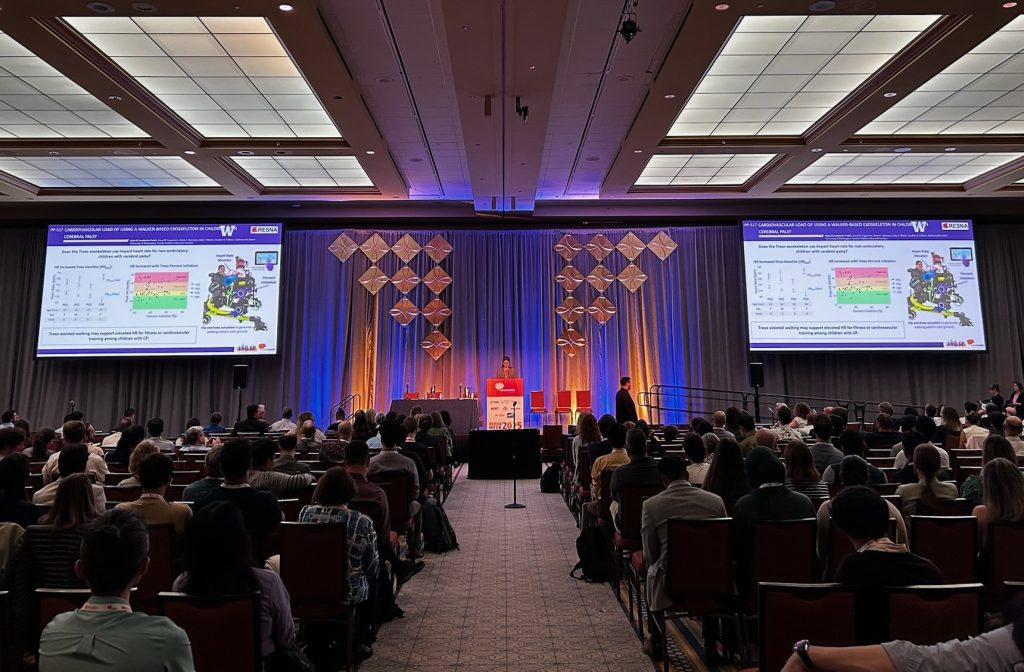
The Neuromechanics & Mobility Lab had a fantastic showing at the 2025 American Society of Biomechanics (ASB) Annual Meeting in Pittsburgh, PA! From student awards to impactful presentations, our team contributed to advancing the science of human movement and rehabilitation engineering.
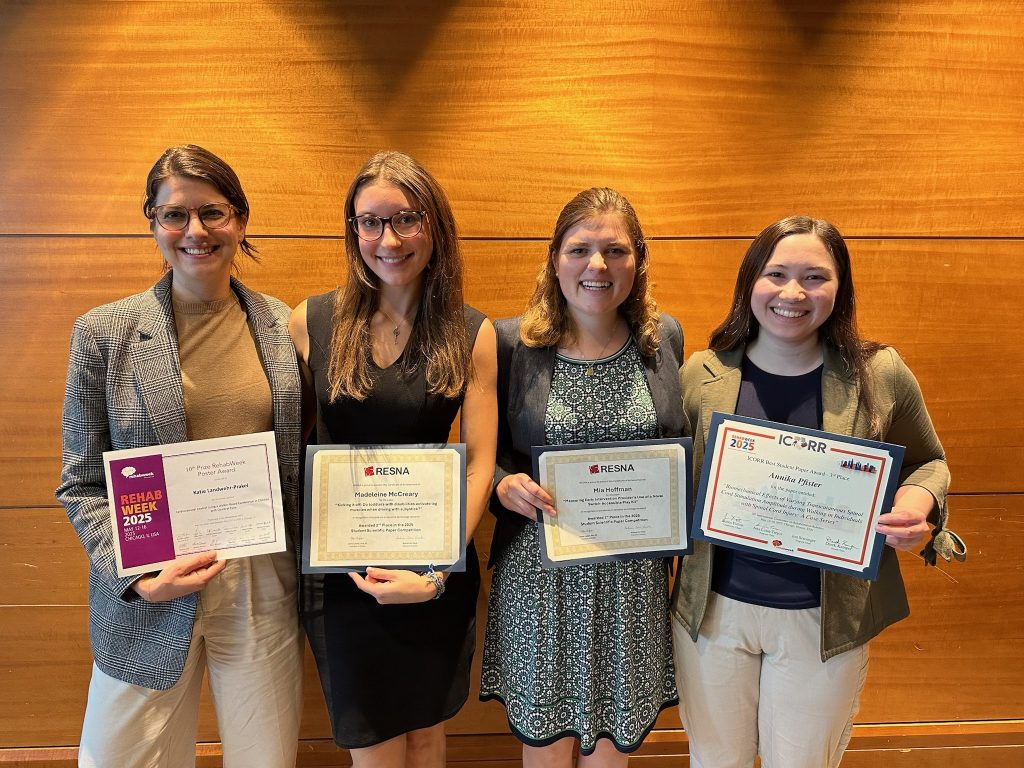
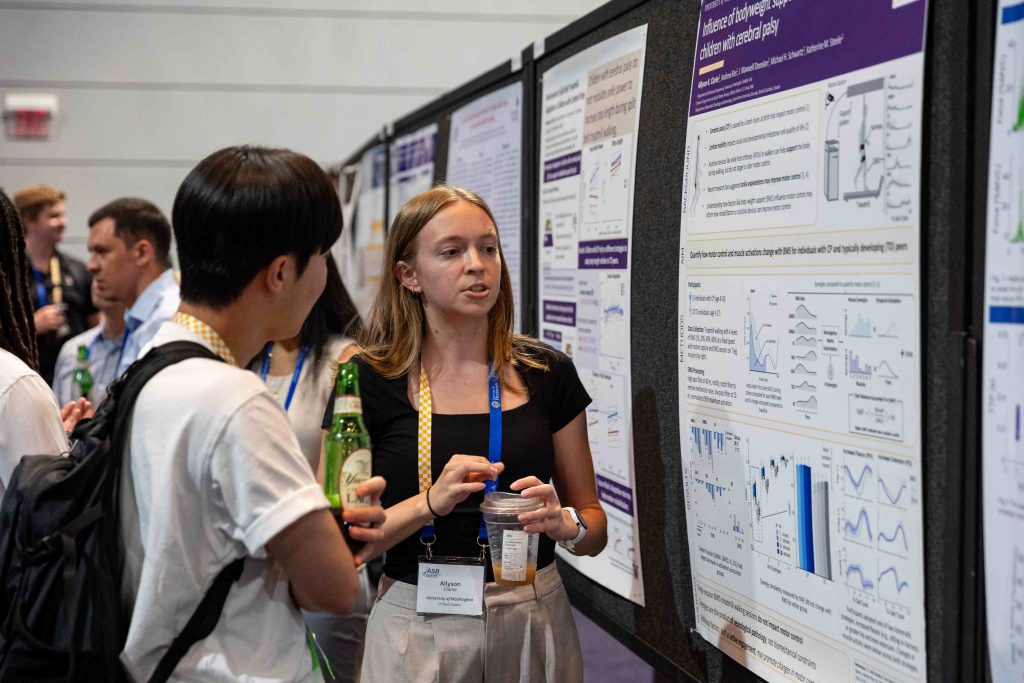
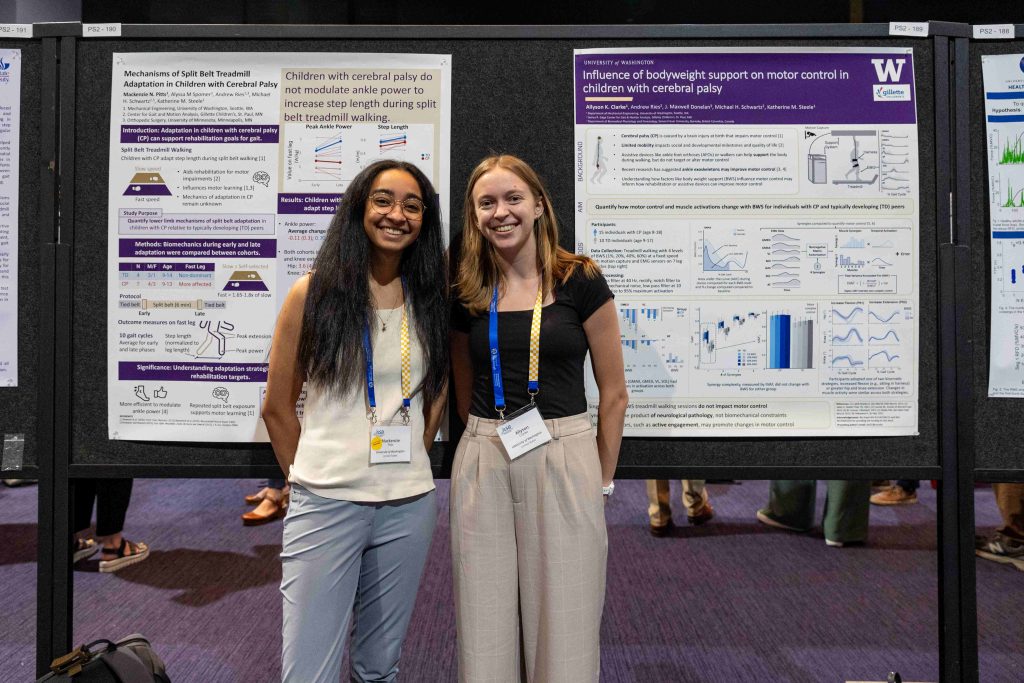
We’re proud to celebrate Ally Clarke, who received a Student Travel Award for her abstract titled “Influence of Bodyweight Support on Motor Control in Children with Cerebral Palsy.” Her work was recognized by the ASB community for its contribution to pediatric motor control research. Congratulations, Ally!
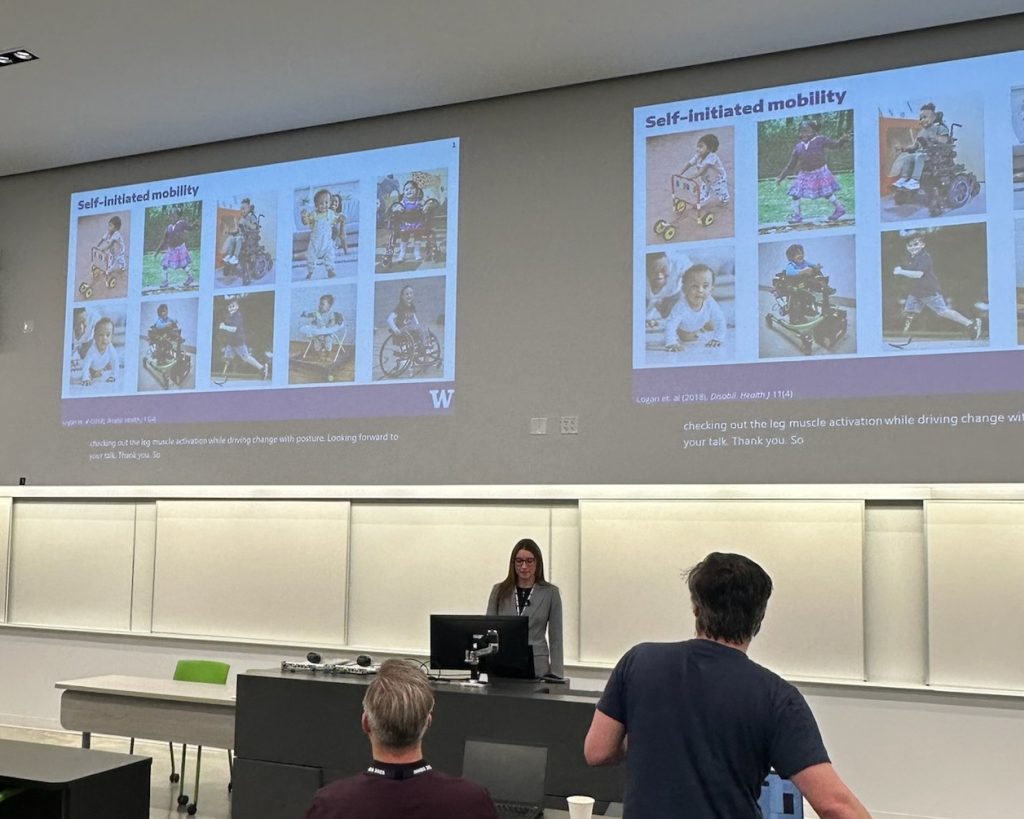
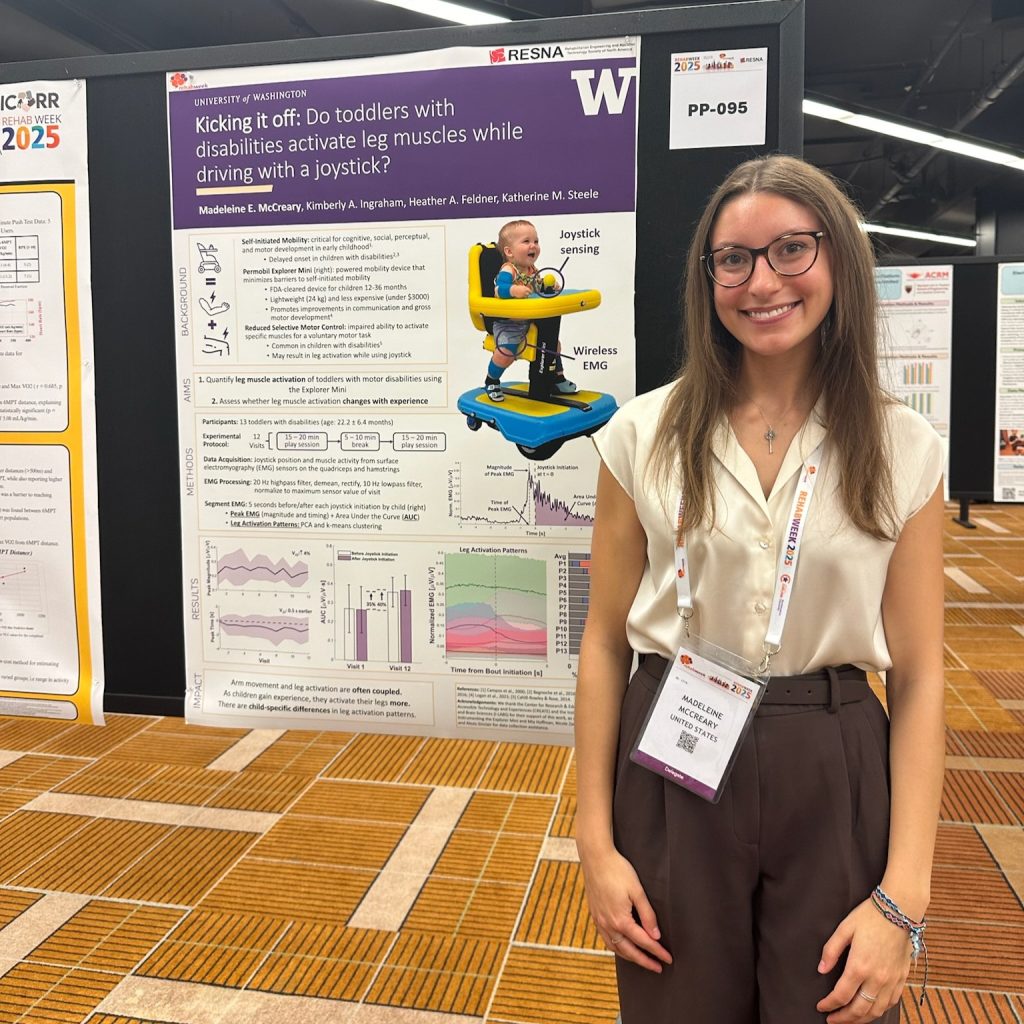
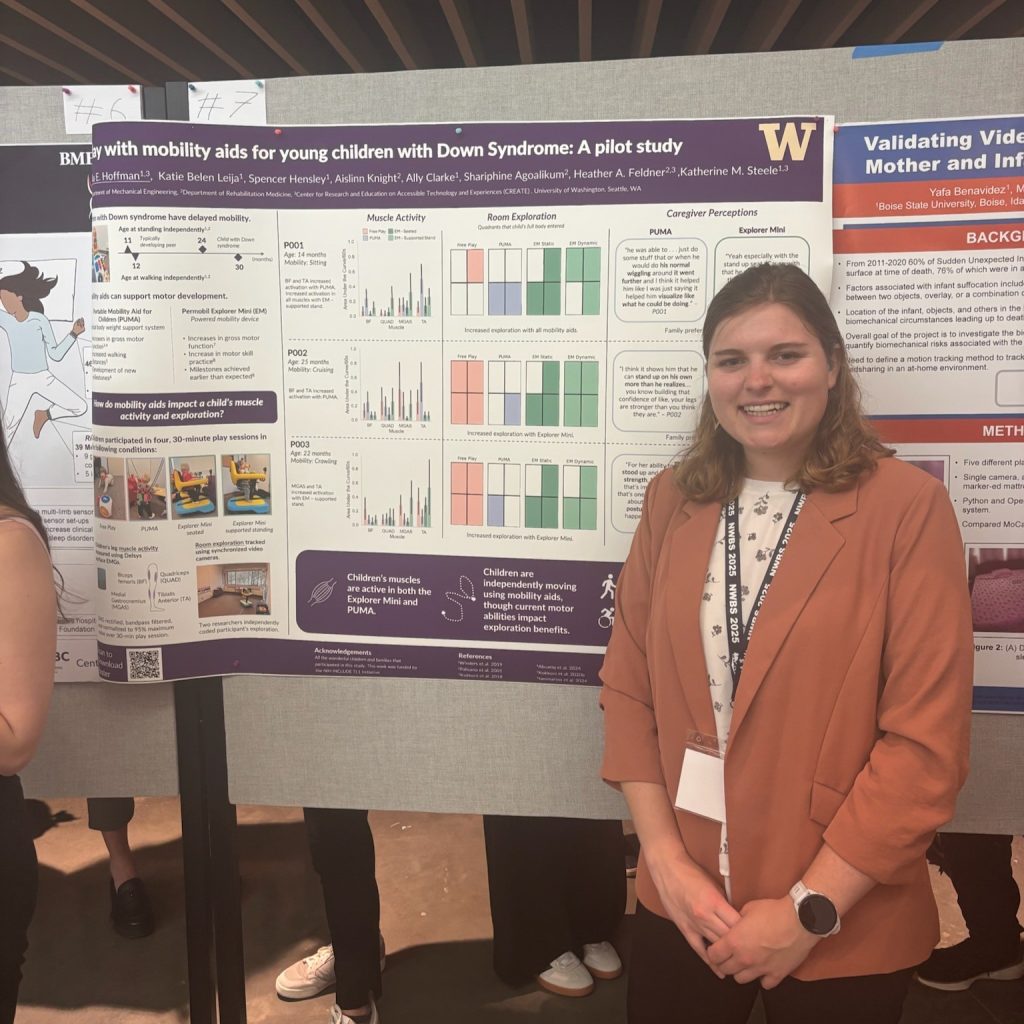
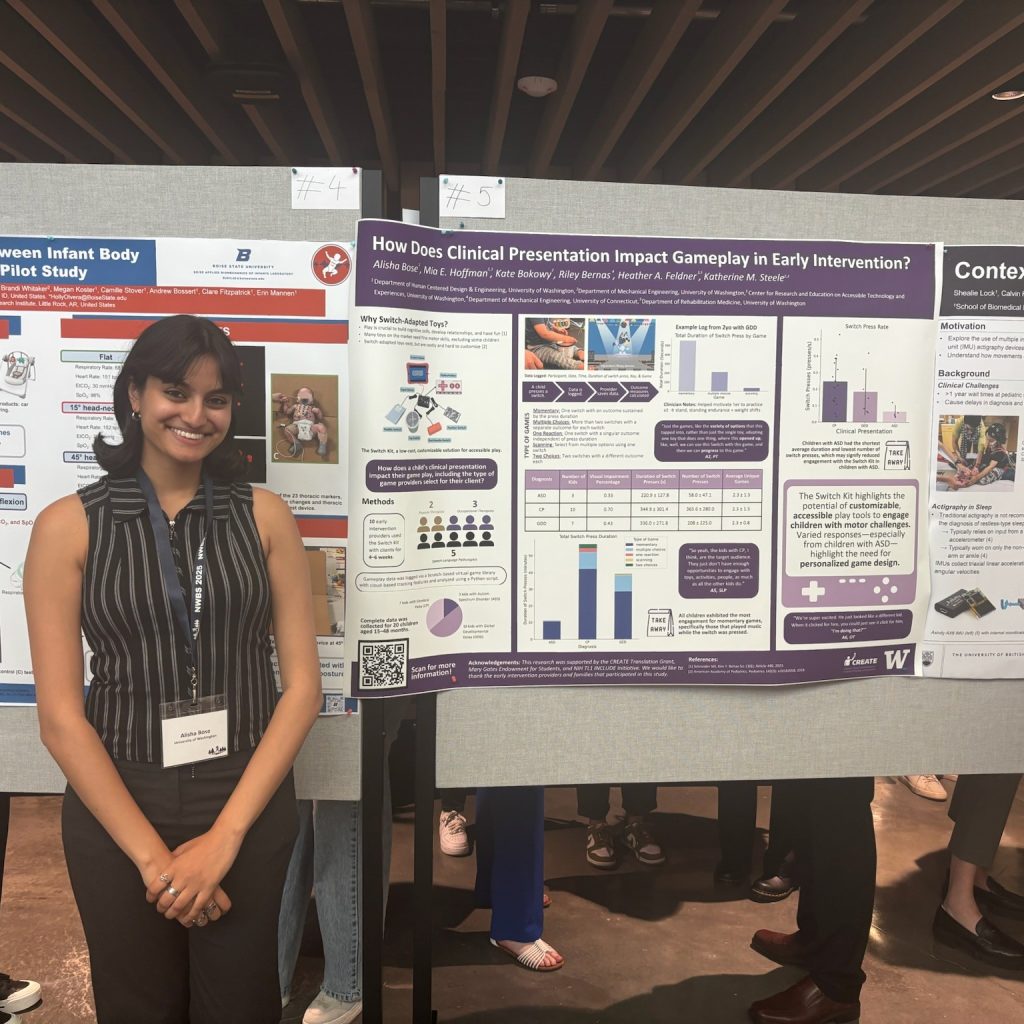
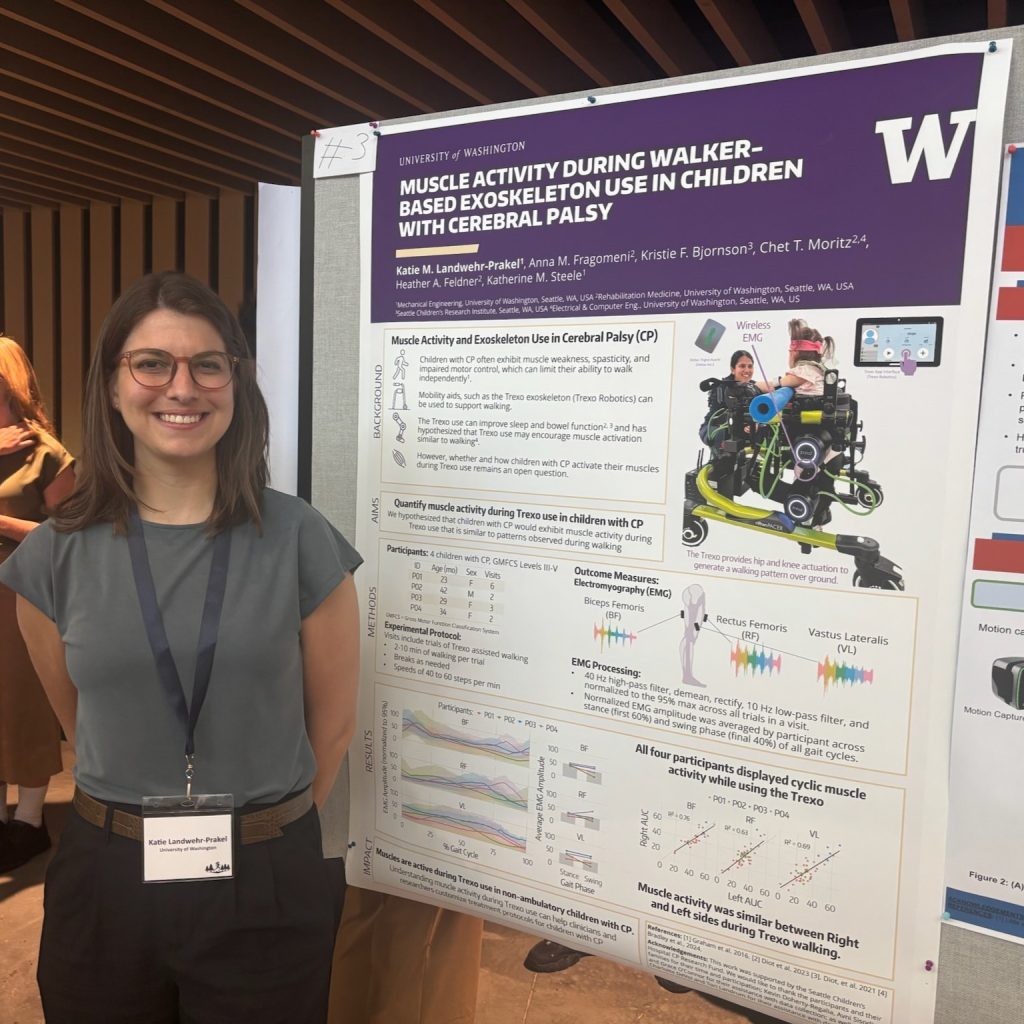
Lab members presented posters across multiple themes. Madeleine McCreary explored toddler muscle activation during joystick driving in her poster “Kicking it off: Does toddler leg muscle activation while driving change with posture?” Mackenzie Pitts shared insights on “Mechanisms of split-belt treadmill adaptation in children with cerebral palsy.” Ally Clarke presented her award-winning work on bodyweight support and motor control, and Katie Landwehr-Prakel showcased her research on “Muscle activity during walker-based exoskeleton use in children with cerebral palsy.”
Beyond the science, our team engaged in workshops, debates, and networking events that emphasized advocacy, inclusion, and the integration of lived experiences into biomechanics research. The ASB 2025 program featured sessions on AI in biomechanics, wearable tech, and neuromechanics – all aligning with our lab’s mission to enhance mobility and participation.
Thank you to ASB and the biomechanics community for an inspiring week. We’re already looking forward to connecting again at the World Congress of Biomechanics (WCB) in Vancouver in 2026!